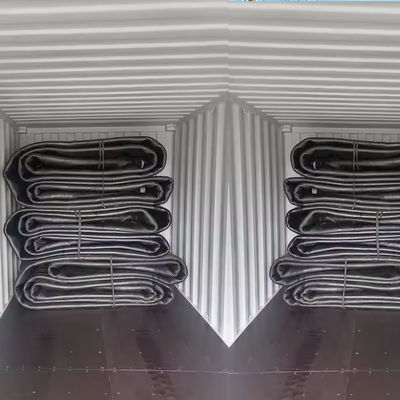
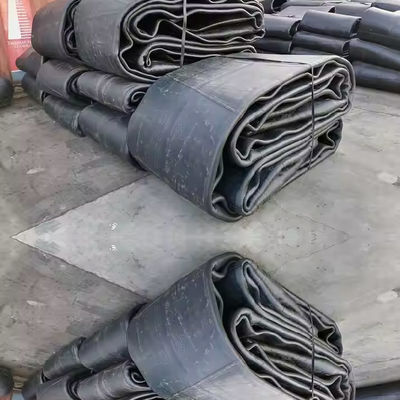
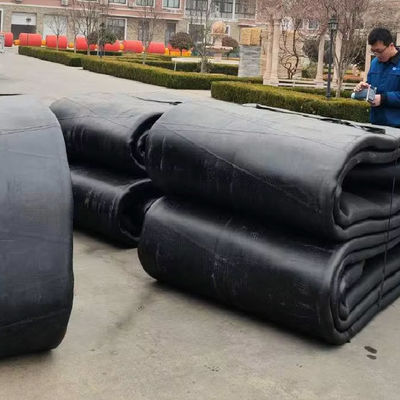
High Bearing Airbag Launching Ship Capacity Durable Floating Marine Rubber Airbags
Description
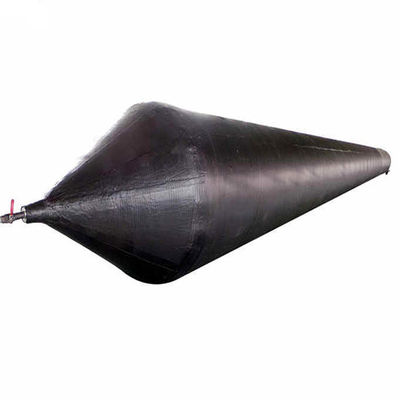
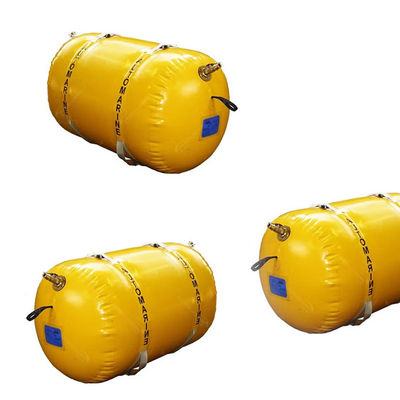
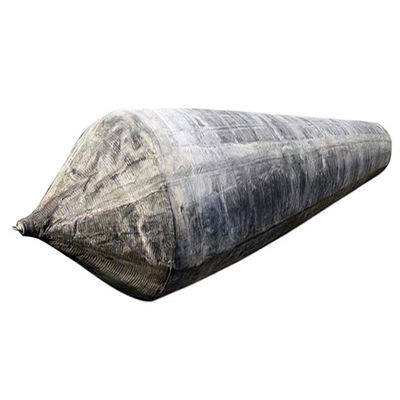
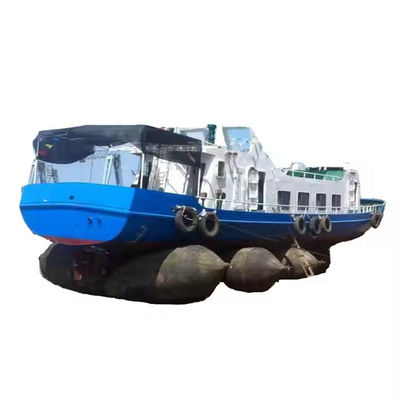
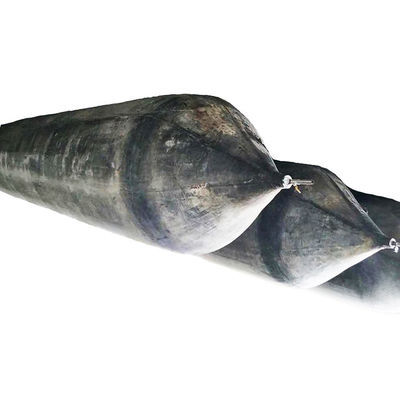
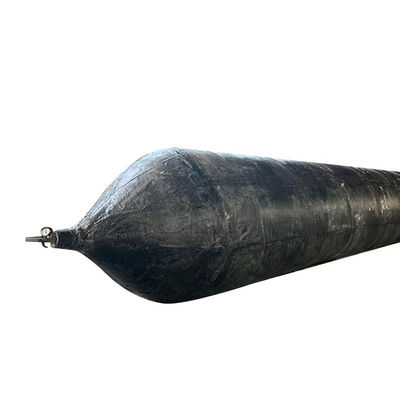
Airbag launching technology represents a groundbreaking innovation in the maritime industry, offering a flexible, cost-effective, and safe solution for launching vessels into the water. This method utilizes heavy duty rubber airbags, strategically positioned under the hull of a ship. Once inflated, these airbags provide the necessary buoyancy and support to lift the vessel smoothly, enabling it to slide gently into the water.
One of the key advantages of airbag launching is its adaptability. It is suitable for various ship types, including cargo ships, fishing vessels, yachts, and even large offshore platforms. Unlike traditional methods such as slipways or cranes, airbag launching requires minimal infrastructure and can be performed in diverse environments, from coastal shipyards to remote locations with limited facilities.


Specifications
| Item |
Description |
| Place of Origin |
China |
| Brand Name |
Hongruntong Marine |
| Model Number |
HM-ALS064 |
| Material |
Industrial-Grade Natural Rubber |
| Diameter |
0.5m-3.0m, or as Request |
| Length |
1.0m-28.0m, or as Request |
| Working Pressure |
0.05-0.25 mpa |
| Technics |
High pressure, overall winding, explosion-proof |
| Use |
ship launching and docking |
| Thickness |
5-13 ply |
| Standard |
Conducted by ISO14409 and GB/T1590-2006 system. |
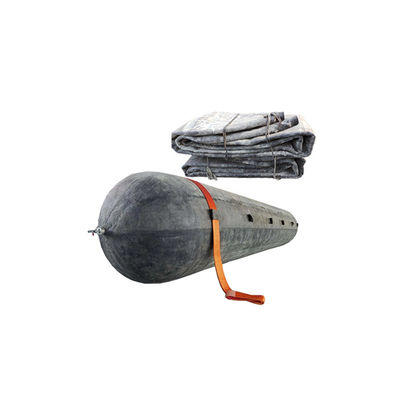
| Accessories |
Q355/SS304/SS316, Pressure Gauge, Tee, Plug, Switch, Inflation Tube |
| Packaging |
Inner-Plastic Bag; Outer-Standard Wooden Pallets. |
| Keywords |
Airbag Launching Ship |
| Certificates |
ABS, BV, KR, LR, GL, NK, RINA, DNV, RMRS |
| MOQ |
1 |
| OEM |
Welcome |
| Diameter |
Working
Pressure
|
Working
Height
|
Bearing Capacity |
| KN/m |
Ton/m |
| D=1.0m |
0.14Mpa |
0.6m |
87.96 |
8.98 |
| 0.5m |
109.96 |
11.22 |
| 0.4m |
131.95 |
13.46 |
| D=1.2m |
0.12Mpa |
0.7m |
94.25 |
9.62 |
| 0.6m |
113.10 |
11.54 |
| 0.5m |
131.95 |
13.46 |
| 0.4m |
150.80 |
15.39 |
| D=1.5m |
0.10Mpa |
0.9m |
94.25 |
9.62 |
| 0.8m |
109.96 |
11.22 |
| 0.7m |
125.66 |
12.82 |
| 0.6m |
141.37 |
14.43 |
| 0.5m |
157.08 |
16.03 |
| D=1.8m |
0.09Mpa |
1.1m |
98.96 |
10.10 |
| 1.0m |
113.10 |
11.54 |
| 0.9m |
127.33 |
12.98 |
| 0.8m |
141.37 |
14.43 |
| 0.7m |
155.51 |
15.87 |
| 0.6m |
169.65 |
17.31 |
| D=2.0m |
0.08Mpa |
1.2m |
100.53 |
10.26 |
| 1.1m |
113.10 |
11.54 |
| 1.0m |
125.66 |
12.82 |
| 0.9m |
138.23 |
14.11 |
| 0.8m |
150.80 |
15.39 |
| 0.7m |
163.36 |
16.67 |
| 0.6m |
175.93 |
17.95 |
| * Other size can be produced follow client's requirements. |
Features
Cost Effective
Reduces overall costs compared to traditional launching methods.
Efficient
Streamlines the launching process, saving time and resources.
Versatile
Suitable for a variety of ship types, from small boats to large vessels.
Adaptable
Can be used in different shipyard environments, including remote locations.
Applications
● Launching in environmentally sensitive areas
● Mobile shipbuilding units
● Temporary shipyards
● Fast deployment operations
Advantages
Over 30 Years of Experience
Extensive industry knowledge and craftsmanship.
Proven Expertise
Recognized as a trusted leader in airbag launching technology.
High-Quality Manufacturing
Strict quality control processes ensure exceptional product standards.
Advanced Production Technology
Utilization of state of the art equipment and techniques.

FAQ
1. What is airbag launching technology?
Airbag launching uses rubber airbags to lift and launch ships into the water.
2. How does the airbag launching process work?
Inflated airbags are placed under the ship’s hull to provide buoyancy and allow controlled launching.
3. What are the benefits of airbag launching?
It is cost-effective, safe, environmentally friendly, and adaptable.
4. What types of ships can be launched with airbags?
It works for cargo ships, fishing boats, yachts, and military vessels, among others.

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!